Chest Physiotherapy Contraindications
Chest Physiotherapy During Mechanical Ventilation
Patients can experience loss of spontaneous breathing when they have to be under mechanical ventilation. This can predispose the patients to developing lung collapse and ventilator-associated pneumonia. In such circumstances, chest physiotherapy can be used to reduce the length of stay in both a mechanical ventilator and ICU and prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia ( ). The high-frequency, chest wall oscillation of intubated patients also resulted in an increase in dry sputum weight (PaO) on day three and decreased lung collapse in days 2 and 3. On day 3, culture positivity improved on day 3 ( ). Similarly, in a patient who received 11 sessions of physical therapy consisting of upright body positioning, mobilization and exercise, and the active cycle of breathing exercise technique every 2 h for 12 h over his 48-h stay in the ICU (six sessions on day one and five sessions on day two), arterial oxygen level improved markedly, with radiographic resolution of infiltration ( ). Since chest physiotherapy can reverse pathological progression and prevent atelectasis as well as improving impaired gas exchange and decreasing culture positivity (which are some of the hallmarks of COVID-19), it is possible to be used in patients suffering from this condition.
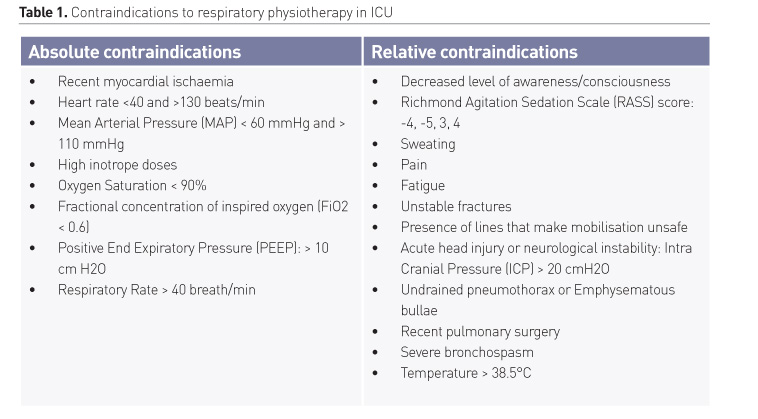
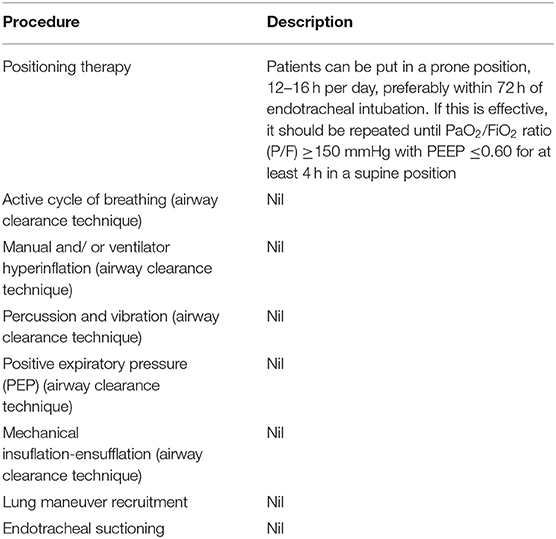
Accordingly, the techniques recommended in patients who are on a ventilator include airway clearance techniques, lung maneuver recruitment, endotracheal suctioning, and change in posture ( ). The airway clearance techniques recommended include positioning, active cycle of breathing, manual and/or ventilator hyperinflation, percussion and vibration, positive expiratory pressure (PEP), and mechanical insuflation-ensufflation ( ). However, there are no details on how to perform these techniques aside from positioning therapy, and there have been no studies yet in patients with COVID-19 reporting on the efficacy of the techniques. Details of positioning therapy can be found in Table 1. In addition, lung maneuver recruitment needs to be used with caution since it may have severe adverse effects ( ). Also, the state of patients’ respiratory, cardiovascular and neurological functions will determine whether chest physiotherapy should be performed during this period. Please refer to Table 2 for more details on contraindications and indications.
Chest Therapy During Mechanical Ventilation
The patient may not be able to breathe spontaneously if they are under mechanical ventilation. This can predispose the patients to developing lung collapse and ventilator-associated pneumonia. In such circumstances, chest physiotherapy can be used to reduce the length of stay in both a mechanical ventilator and ICU and prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia ( ). In addition, high-frequency chest wall oscillation for intubated patients resulted in increased dry sputum weight and PaO on day 3, decreased lung collapse on days 2 and 3, and culture positivity on day 3 ( ). In a similar vein, a patient who had received 11 sessions physical therapy (six on day one, five on day two) showed an improvement in arterial oxygen. This was in conjunction with radiographic resolution for infiltration. Because chest physiotherapy prevents or reverses progression of COVID-19’s symptoms, impairs gas exchange, lowers culture positivity, and helps to reduce atelectasis (which is also a hallmark of COVID-19), patients can use it.
For patients with ventilators, airway clearance techniques include lung maneuver recruitment, endotracheal vacuuming and change in position (). The airway clearance techniques recommended include positioning, active cycle of breathing, manual and/or ventilator hyperinflation, percussion and vibration, positive expiratory pressure (PEP), and mechanical insuflation-ensufflation ( ). These techniques are not detailed, nor is there any evidence of their effectiveness in COVID-19 patients. For more information on positioning therapy, please refer to the following. You should also be cautious when using lung maneuver recruitment as this could have adverse side effects. Additionally, the state of the patient’s respiratory, cardiovascular and neurological systems will determine whether chest physiotherapy should be performed during this time. See for details of the indications and the contraindications.
.Chest Physiotherapy Contraindications
Kent Chiro-Med Wellness Clinic
| Website | https://www.kentchiromed.com/ |
| Address | 563 Gladstone Ave, Ottawa, ON K1R 5P2, Canada |
| Phone | +1 613-508-0113 |
| Category | Physiotherapy Ottawa |
Beverly Physiotherapy
| Website | http://www.beverlyphysiotherapy.com/ |
| Address | 747 Ellice Ave, Winnipeg, MB R3G 0B5, Canada |
| Phone | +1 204-774-8385 |
| Category | Physiotherapy Winnipeg |





















:fill(white)

